Search here:
иҪҜ件еҲҶзұ»soft Nouns
- е…¶е®ғ (54)
- ең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件 (39)
- ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件 (35)
- ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件 (126)
- ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ (17)
- ж•°еҖјжЁЎжӢҹиҪҜ件 (34)
- жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件 (98)
- з»ҳеӣҫжҲҗеӣҫ (23)
- йҮҮжІ№иҜ•дә•еҺӢиЈӮ (68)
- й’»дә•жөӢдә•иҪҜ件 (63)
ж Үзӯҫ
- bakerhughes
- BGP
- cggveritas
- geomodeling
- geotomo
- greenmountian
- IHS
- ikon
- landmark
- landocean
- linux
- midland-valley
- paradigm
- Schlumberger
- Weatherford
- win32
- win64
- ең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件
- ең°йңҮеӨ„зҗҶ
- ең°йңҮи§ЈйҮҠ
- ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ
- еҹ№и®ӯи§Ҷйў‘
- ж•°еҖјжЁЎжӢҹ
- жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件
- з»ҳеӣҫжҲҗеӣҫ
- иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
- йҮҮжІ№иҜ•дә•еҺӢиЈӮ
- й’»дә•жөӢдә•
- йқһең°йңҮ
-
жңҖиҝ‘жӣҙж–°update
- The Kingdom Software 2023 smt 2023
- QUE$TOR 2023 Q1
- Harmony Enterprise 2023.1
- GOHFER9.4.0.32 20230407
- JewelSuite GeoMechanics 2022.2
- Eliis PaleoScan 2022.2
- Flatirons™ Software Products
- OpendTect 6.6.10
- OpendTect 6.6.8
- ResFormSTARжңҖж–°зүҲ2023
- еҜҶз ҒдҝқжҠӨпјҡSchlumberger Techlog 2020 2021 2022
- WellFlo 6.9
- VECON 4.7 2022
- SKUA-GOCAD 2022
- vista 2022
- stimpro 2022
- pvtsim Nova 6.0
- Kingdom software SMT 2022
- NETool 10.9
- PerGeos 2022
- FracPT 2022
- OpenFlow 2022
- OLI systems 9.6.3
- norsar 2023
- еҜҶз ҒдҝқжҠӨпјҡpetrel 2022
- QUE$TOR 2022
- gohfer 9.3 64bit е®ҢзҫҺзүҲ
- Paradigm 2022
- Landmark DSG 10ep5
- Geosoftware jason 12.0 2023
- Interoctive Petrophysics 5.1 2023
- landmark EDT 5000.17.2 2023
- redhatВ зүҲжң¬дёҺеҶ…ж ёеҜ№еә”
- Schlumberger Omega 2022.1
- Landmark Promax seisspace 5000.11.0.1
- Greenmountain MESA16.3.5
- tNavigator 2022.4
- GeoSoftware HRS 13.0 2023
- IP 5.0 2023
- Cerberus 14.5
- InterWell 2019.1
- tNavigator 2020.1
- norsar 2020
- forward.net 3.0
- IHS welltest 2019
- IHS Harmony 2019
- The Kingdom Software 2019 smt
- DynaLift
- permedia 5000
- StrataBugs 2.1
- RMS 11.1,RMS 2023
- Geogrid 1.19
- Tempest Enable 8.5
- sysdrill 11
- OpenInvertor 10.3.0 windows linux all full
- жІ№ж°”и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢдёҺеҠЁжҖҒеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件 restools
- norsar 2019 seisrox 2019 MDesign 2019
- forward.net 3.0 2019
- IP 4.5 2019
- gohfer 9.1.3 2019
- DTCC SmartSoloВ®
- JewelSuite 2018.1 GeoMechanics 2018.1.441
- WellCad 5.3
- GPTMap GPTModel GPTLog 2017.1
- opendtect 6.4.4
- Kappa Workstation 5.20.05
- IPM 11
- GeoModeling 2019
- PVTsim Nova 4.1
- tNavigator 19.2
- epoffice 2019.06.10
- PaleoScan 2019.1.0
- PerGeos 2019.1
- geolog 19.0
- pvtsim nova 4.0
- tNavigator 19.1
- Tesseral 5.1.0 2019
- geoscope3.4
- FracproPT 2019
- I-GIS GeoScene3D v10.0.13.574
- Paradigm Geolog 18
- Rokdoc 6.6.2 еІ©зҹізү©зҗҶиҪҜ件
- Lead 3.0 LEAD3.0жөӢдә•еӨ„зҗҶи§ЈйҮҠдёҖдҪ“еҢ–иҪҜ件
- JewelSuite 2017
- promax 5000.10.0.3
- discovery2019.1
- simics 4.8
- Emeraude v5.20 з”ҹдә§жөӢдә•и§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件
- иҫ…еҠ©еҺҶеҸІжӢҹеҗҲиҪҜ件SenEx2.0.40
- tNavigator 18.4
- jason10.0.1
- GeoEast-EasyTrackи§ҰжҺ§и§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件
- hrs 10.4.1
- Landmark EDT 5000.15.1
- Landmark EDT 5000.15.0
- perform 2013
- DecisionSpace_Geosciences-10ep.4.03_G1
- PetroAnalyst 2014
- JewelSuite GeoMechanics 2016.1.364 6.1
- GeoModeller 4.05 2019
- watch 2.8.1 з”ҹдә§жөӢдә•и§ЈйҮҠе№іеҸ°
- discovery 2017.3
- CMG 2018.101
- Emeraude5.12.07
- Simpleware v7.0 ж•°еӯ—еІ©еҝғе»әжЁЎдёҺж•°еҖјеҲҶжһҗи§ЈеҶіж–№жЎҲ
- Greenmountaion mesa 12.1 for win10
- IC 2016
- QUE$TOR 2018.1
- METACOMP 14.1.1 жөҒдҪ“еҠӣеӯҰиҪҜ件
- ORGE 4.0.7.13
- DecisionSpace Geosciences 10ep.3.06
- PetraSim 2018
- Rokdoc 6.6
- RMS 11
- opendtect 6.4
- WinGLink
- GeoModeller 4.04 2018
- tesseral pro 5.06
- Kappa workstation 5.20.02
- Stimpro 2018
- QITeam
- Res2dinv Res3dinv з‘һе…ёй«ҳеҜҶеәҰз”өжі•еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件
- PetraSim 2017.10
- FRACPRO 2017 еҺӢиЈӮи®ҫи®ЎдёҺеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件
- iMOSS 4.3 еІ©зҹізү©зҗҶиҪҜ件
- Cerberus v11.5 иҝһз»ӯжІ№з®ЎиҪҜ件
- FracMan 7.70 7.51
- GeoEast-USPйқһ常规з”ңзӮ№ең°йңҮйў„жөӢиҪҜ件
- Petra 3.12
- geoscope 3.3
- Georeservoir 6.0
- kelang йҮҮйӣҶи®ҫи®ЎиҪҜ件
- PETRA 2017 3.11
- surfseis
- tNavigator 18.2
- pvtsim nova 3
- зҪ‘ж јеӨ©ең° ж·ұжҺўең°еӯҰе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件
- hrs 10.3.2
- omega 2017 2018 2019 2020 2021 2022
- I-GeoSeisV2.0
- jason 9.7.3 powerlog 9.7.3
- ResTools
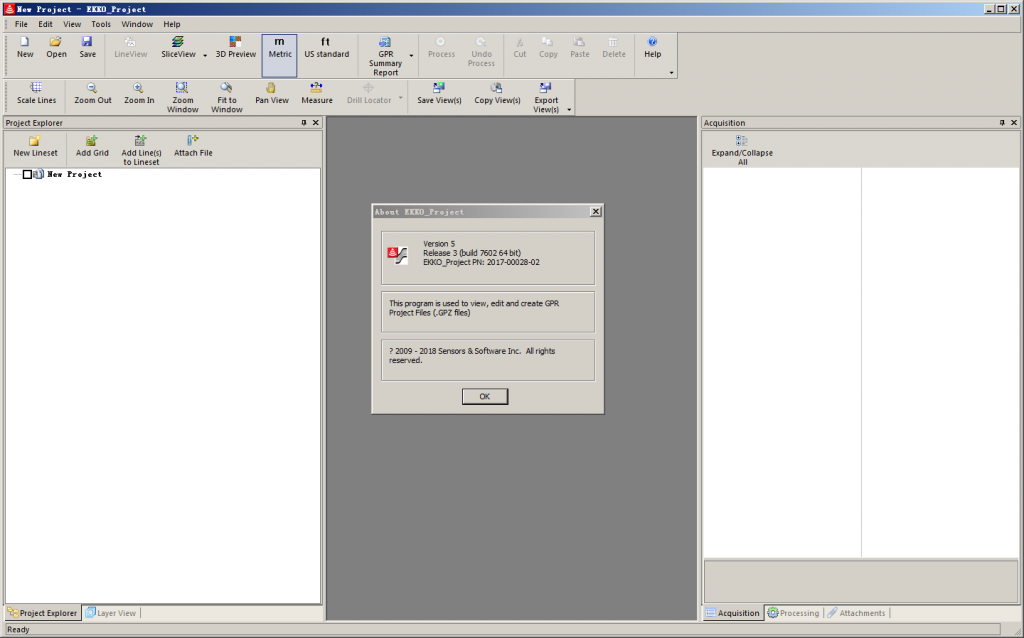
- EKKO_Project-V5-R3-64bit
- Geosec 2018
- Emerson Paradigm 2018.1 2019 2022 2023
- Seisware 9.1
- flatirons 18.02
- Greenmountaion mesa 15
- GMseis 3.4
- tomodel 8.0
- Pegete SMI 3.0
- Sercel e428V5.0
- KAPPA Workstation 5.20
- Seismic Processing Workshop 3.4 SPW 3.4
- Testif-i v2.07a
- epoffice 2017 v7
- TENDDEKA FloQuest 7.5
- TENDEKA ReQuest 7.5
- landmark Nexus VIP
- PaleoScan 2018.1
- Petroleum Experts IPM 10
- jason 9.7.2
- openflow 2017.1
- tNavigator 18.1
- tNavigator 17.4
- PHDwin2.10.3
- meyer 12 2017.12
- HampsonRussell Suite 10.3 geoview 10.3 HRS 10.3
- Midland Valley move 2018.1
- jason 9.7
- CoilCADE
- StimCADE
- crystal 2018.1
- gohfer 9.0.1.6 GOHFERе…Ёдёүз»ҙеҺӢиЈӮеҸҠй…ёеҢ–и®ҫи®ЎдёҺеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件
- еҜҶз ҒдҝқжҠӨпјҡSchlumberger Techlog 2018.2
- omni 2017.1
- tesseral pro 5.0.3b
- CMG 2017.101
- Schlumberger vista 2017
- GeoModeller 4
- KAPPA Workstation 5.12.04
- metalink
- EarthImager 2D 3D
- Promax 5000.10
- rokdoc 6.5
- tNavigator 17
- Kappa workstation 5.12.03
- Paradigm Sysdrill 10.5 SP1
- PaleoScan 2017.1.0
- tesseral pro 5.02a
- GeoTeric 2017.1
- The Kingdom Software SMT 2017
- refract 3.0
- TADPRO 3.2.1 з®ЎжҹұдёӢе…ҘиҪҜ件
- Geosyn 2016.1
- norsar 201707
- NeuraView NeuraMap NeuraLog NeuraSection 2017
- IHS Kingdom SMT 2016.1
- studioSL 3DSL
- GOHFER 9.0
- tesseral pro 5.0.1
- jason 9.6.1
- DecisionSpace Well Planning
- crystal 2017.1.16
- norsar 2017.1
- ARIES 5000
- GeoTeric 2016.2.1
- geocyber еӨҡеӯҗжіўеҲҶи§ЈиҪҜ件
- TrapTester 7 2016 ж–ӯеұӮе°Ғе өжҖ§иҜ„д»·иҪҜ件
- Landmark EDT 5000.14.1
- Paradigm Geolog 8.0
- Paradigm 2017
- Emeraude – Production Logging
- LESA 2017
- geomap 4.0
- LogIC
- rokdoc 6.4.2
- PIPEFLO 9.5.6.3
- IHS FAST VisualWell
- IHS welltest 2016
- ResForm GeoOffice 3.2е®ҢзҫҺзүҲ 3.5е®ҢзҫҺзүҲ
- ModelVision йҮҚзЈҒж•°жҚ®еӨ„зҗҶеҸҚжј”иҪҜ件
- CRYSTAL PROD 2017.1
- KAPPA Workstation 5.12
- Geographix DISCOVERY GVERSE Attributes 2016.1
- Geographix GeoGraphix discovery 2016.1
- 3DSL 2012 2014
- WellCAD жөӢдә•еӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件
- Midland Valley Move 2017.1.1
- prism Interpret 2014
- wellscan 3.5
- Geoteric 2016.2
- WellWhiz 3.4
- GOHFER 8.4.0
- FRACPRO еҺӢиЈӮи®ҫи®ЎдёҺеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件
- Ecrin 5.10.04
- DSS Dynamic Surveillance System жІ№и—ҸеҠЁжҖҒжЁЎжӢҹиҪҜ件
- sendra еІ©еҝғж•°еҖјжЁЎжӢҹиҪҜ件
- LCT йҮҚзЈҒйңҮиҒ”еҗҲеӨ„зҗҶи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件
- mesa 14.1
- jason9.6
- HRS10.2
- SegdToolbox
- justcgm
- ImageToSEGY
- WellView
- ең°йңҮж•°жҚ®ж•°еӯ—еҢ–иҪҜ件 bmp2segy 3.0
- Senergy Interactive Petrophysics v4.4 IP4.4
- еҜҶз ҒдҝқжҠӨпјҡSchlumberger CemCade 4.4 4.75еӣәдә•иҪҜ件
- CMG 2016.10
- VISTA 2016.000
- PVTsim20
- Dynel 2D Dynel 3D
- Gxplorer 2016 зҹіж–ҮиҪҜ件 2016
- GOHFER 8.3.1.2
- cgg geovation 2015 6501 cgg geovation 2016 6601 geovation 2.0 2.1(2020) 2.2 (2022)
- norsar 2016.1
- norsar 2016.1 windows and linux
- drillbench2016.1.1
- crystal 2016.2
- move 2016.2.2
- petra 3.10
- Depth Insight 2015 зҪ‘ж јеӨ©ең° ж·ұжҺўең°еӯҰе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件
- IHS Harmony 2016.3
- tesseral pro 4.2.4
- rokdoc6.3.3
- JewelSuite GeoMechanics
- drillbench2016.1
- GeoTeric 2016.1 еҹәдәҺең°иҙЁеҜјеҗ‘ең°йңҮеғҸзҙ жі•зҡ„жІ№и—ҸжҸҸиҝ°иҪҜ件
- IHS Harmony 2016.1
- jason 9.5.1
- velpro
- TRC Phdwin v2.9 1CD(еӮЁеӨҮе’Ңз»ҸжөҺиҜ„д»·иҪҜ件)
- SurvOPTжө·жҙӢең°йңҮеӢҳжҺўзҡ„规еҲ’е’ҢжҲҗжң¬и®Ўз®—е·Ҙе…·
- Landmark EngineerвҖҷs Desktop(EDT) 5000.14
- GPTmodel
- GPTmap
- GPTlog
- Pipe Flow Expert
- Direct ж•°еӯ—еҢ–жІ№и—ҸиЎЁеҫҒиҪҜ件系з»ҹ
- Dionisos4.0 4.2
- SeisRox дёүз»ҙжЁЎеһӢжӯЈжј”
- ZetaWare
- Intrepid Geophysics GeoModeller дёүз»ҙең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件
- forward forward.net
- easycopy
- beicip easytrace
- SPT wellflo
- Weatherford Field Office 2014 PanSystem 2014
- universe VSP
- Secure Hydraulics 2011 е®үе…Ёж¶ІеҺӢиҪҜ件
- fracman 7.0 7.4 7.5.1 2016
- copy+
- SeisMod 4 SIMO4.2
- Green Mountain mesa 12 13 14
- powerlog frac 9.5
- PaleoScanе…ЁеұҖиҮӘеҠЁең°йңҮеұӮеәҸең°еұӮеӯҰи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件 2016.1
- powerlog 9.5
- jason9.5
- opendtect6.0.1
- Midland Valley move 2016.1
- imoss 3.4
- discovery 2015
- geomodeling attributestudio 8.0
- geolog7.4
- OpenInventor 10.3.0
- GeoTomo VECON
- OLGA 2015.1
- еҜҶз ҒдҝқжҠӨпјҡSchlumberger techlog 2015.2 techlog 2015.3 techlog 2016
- comet3
- norsar 2d 3d
- skua gocad 2015
- iMOSS 3.3 2015
- insiteеҫ®ең°йңҮиҪҜ件
- Petrosys 17.5 17.6 17.7
- Petroleum Experts IPM 9.0
- RODSTAR-V/D жҠҪжІ№жңәи®ҫи®ЎиҪҜ件
- IHS Harmony 2015.2
- PLOT EXPRESS zeh 5.1
- insight Earth 3.0
- jason 9.0 2015 linux
- еҸҢзӢҗ doublefox еҸҢзӢҗеҸҳйҖҹжҲҗеӣҫзі»з»ҹ 4.0 2014
- crystal specman thinman 2015.1
- NeuraLog 2015.4
- landmark DecisionSpace DSD 5000.10.03 5000.10.04 linux
- GOGEO FracPredictor 2014
- paradigm epos geodepth gocad skua geolog sysdrill StratEarth 2015
- jason 9.0 jason 9.1 2015
- hrs strata geoveiw 10.1жӯЈејҸзүҲ 2015 10.1 20160308жӯЈејҸзүҲ
- NEToolе®Ңдә•дјҳеҢ–и®ҫи®ЎиҪҜ件
- landmark DSD Geoprobe 5000.8.3 5000.10 windows linux
- discovery 2014.2
- powerlog\powerbench\PowerlogFrac 3.5
- meyer2014 english version +дёӯж–ҮзүҲ
- omni 2014
- vista 2014 vista 2015
- Senergy Interactive Petrophysics v4.3 v4.4 IP4.3 IP4.4
- Emeraude v2.60.12
- ecrin4.30.07 Citrine Saphir Topaze Emeraude Azurie
- landmark 5000.10
- landmark 5000.10 windows
- openflow 2012 2013 2015 2015.3
- SpecMAN
- geomodeling attributestudio 7.5
- Gxplorerзҹіж–ҮиҪҜ件
- neuralog
- LogVision
- INTViewer
- NetSarang Xmanager Enterprise 5.0.0464
- jason 8.4.2 |1 dvd
- powerlog 3.4.5
- move 2015.1
- JewelSuite Subsurface Modeling 2014
- Landmark Engineer’s Desktop(EDT)
- Marvel еҸ еүҚең°йңҮжҲҗеғҸзі»з»ҹ пјҲиҖҒзүҲжң¬еҗҚз§°дёәViewsпјү
- promax 2003 5000 5000.8 5000.10
- GRISYSең°йңҮж•°жҚ®еӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件系з»ҹ
- omega2013.1
- tNavigator 3.3 tNavigator 4.1 tNavigator 4.2вҖ“жІ№и—Ҹж•°еҖјжЁЎжӢҹзі»з»ҹ
- Seismic Studio жҠҳе°„еҸҠеұӮжһҗйқҷж ЎжӯЈиҪҜ件
- WellFlo еҚ•дә•йҮҮжІ№дјҳеҢ–дёҺи®ҫи®ЎиҪҜ件
- Eps PanSystem V2014 иҜ•дә•и§ЈйҮҠеҲҶжһҗдёҺи®ҫи®Ў
- Schlumberger.SandCADEйҳІз ӮиҪҜ件
- Schlumberger.FracCADEеҺӢиЈӮи®ҫи®ЎдёҺиҜ„д»·иҪҜ件
- E-stimplan е…Ёдёүз»ҙж°ҙеҠӣеҺӢиЈӮиҪҜ件
- еӨҚжқӮжҺўеҢәиҝ‘ең°иЎЁе»әжЁЎе’Ңж ЎжӯЈзі»з»ҹToModel6.5 7.0 8.0
- drillinginfo transform 4.3.1 5.0.2 еҫ®ең°йңҮиҪҜ件
- GMSeis3.1 GMseis3.2 GMseis3.4 ең°йңҮиҝ‘ең°иЎЁйқҷж ЎжӯЈзі»з»ҹ seislab
- GMI ең°еә”еҠӣеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件
- еҸҢзӢҗиҪҜ件
- Oasis montajйҮҚзЈҒйңҮеӢҳжҺўиҪҜ件еҢ…
- GeoEast 2.5 2.6.1 2.6.2 2.6.3 3.0
- EPoffice image+
- EPoffice EPS+
- EPoffice FRS+
- EPoffice GeoTalk
- GOHFER 8.1.1 8.2.3
- SeisWare8.00.05
- Hampson-Russell HRS strata
- tesseral tesseral3D
- GeoModeling VisualVoxat (VVA)
- discovery еҫ®жңәи§ЈйҮҠзі»з»ҹ
- basinmod 2005 2009 2012 2014
- Kingdom SMT
- JewelSuite2013 2014
- GeoThrust дәҢз»ҙгҖҒдёүз»ҙең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶзі»з»ҹ
- PaleoScanе…ЁеұҖиҮӘеҠЁең°йңҮеұӮеәҸең°еұӮеӯҰи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件
- petra
- FracproPT 2012 FracproPT 2013 FracproPT 2015 FracproPT 2017
- Meyerдёүз»ҙеўһдә§жҺӘж–ҪжЁЎжӢҹи®ҫи®Ўзі»з»ҹ
- CMG2012 2013.11 2014.10 2015.101 2015.106
- SPSQC
- RokDoc
- LESA 9.5 9.6 9.7
- Recon
- FaultX
- NorSar
- METALINK
- MOVE 4.1 5.0 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014.1 2014.2
- landmark openworks 2003 5000.3 5000.8.1 5000.8.3
- TomoPlus
- CycloLog
- iMOSS 3.1 3.2
- SeisUP 2008 2009 2010 2011 2012 2013 2014
- RMSең°иҙЁдёүз»ҙе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件
- Drillworks
- Drillnet
- зҹіжІ№иҪҜ件зҡ„Redhat ASеҗ„зүҲжң¬дёӢиҪҪең°еқҖ
- CRYSTALең°йңҮеҸҚжј”еҸҠең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件
- jason8.4
- Ecrin 4.20.5 4.30 4.30.07 5.10.02
- PowerLog 3.4.1
- tesseral pro 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.2.1 4.2.2 4.2.4
- Tempest-Enable
- sysdrill
- SPTGROUP.DrillBench 6.2 2016.1 й’»дә•еҸҠе®Ңдә•е·ҘзЁӢи®ҫи®ЎжЁЎжӢҹиҪҜ件 6.2 2016.1
- Paradigm 2011.2 её•жӢүд»Је§Ҷ Epos 2011.3 2013.2 2014.1 2014.1sp1 2015.1 2015.5
- EchosпјҲFOCUSпјүең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶзі»з»ҹ
- ең°йңҮжіўеҸҚе°„зҡ„жһҒжҖ§зӣёдҪҚй—®йўҳ
- OLGA 7.1* 7.2* 7.3* 2014.1 2014.2 2014.3
- GeoTericеҹәдәҺең°иҙЁеҜјеҗ‘ең°йңҮеғҸзҙ жі•зҡ„жІ№и—ҸжҸҸиҝ°иҪҜ件(SVI)
- CGG geovation cgg3100 cgg4100 cgg5000 cgg6200 cgg6401 cgg6501 cgg6601 geovation2013 geovation 2015 geovation 2016
- STIMPRO еҹәиҙЁй…ёеҢ–и®ҫи®ЎдёҺеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件
- GEOLOG
зү№еҲ«еЈ°жҳҺ
жң¬з«ҷдёҘзҰҒжҸҗдҫӣд»»дҪ•еёҰиүІ жғ…пјҢиҝқ жі• еҶ… е®№зҡ„иҪҜ件пјҒж¬ўиҝҺеӨ§е®¶зӣ‘зқЈпјҢжңүй—®йўҳеҸҜеҸ‘йӮ®д»¶з»ҷз«ҷй•ҝ.жң¬з«ҷжүҖжңүиө„жәҗжқҘжәҗдәҺзҪ‘еҸӢдәӨжөҒ,еҸӘдҫӣзҪ‘з»ңжөӢиҜ•гҖҒиҜ·еңЁ24е°Ҹж—¶еҶ…еҲ йҷӨжүҖдёӢеҶ…е®№пјҢејҖе§Ӣжё…зҗҶж— зүҲжқғзҡ„еҶ…е®№пјҢиҜ·еӨ§е®¶ж”ҜжҢҒжӯЈзүҲ пјҒ
е…ідәҺжң¬з«ҷ
1.жң¬з«ҷжүҖжңүиө„жәҗВ жҗңйӣҶдәҺдә’иҒ”зҪ‘жҲ–з”ЁжҲ·иҮӘиЎҢеҸ‘еёғпјҢжң¬з«ҷжңҚеҠЎеҷЁдёҚеӯҳеӮЁд»»дҪ•иө„ж–ҷ;
2.жң¬з«ҷжүҖжңүеҸ‘еёғиө„жәҗд»…дҫӣдёӘдәәеӯҰд№ дәӨжөҒ,дёҘзҰҒз”ЁдәҺе•Ҷдёҡз”ЁйҖ”,еҰӮйңҖз”ЁдәҺе•ҶдёҡжҲ–з§‘з ”зӯүиҜ·еҲ°е®ҳж–№иҙӯд№°;
3.еҰӮжң¬з«ҷдёҚж…ҺдҫөзҠҜдҪ зҡ„зүҲжқғ,иҜ·жқҘз”өе‘ҠзҹҘгҖӮжҲ‘们е°Ҷдјҡ第дёҖж—¶й—ҙеҲ йҷӨзӣёе…ій“ҫжҺҘ;
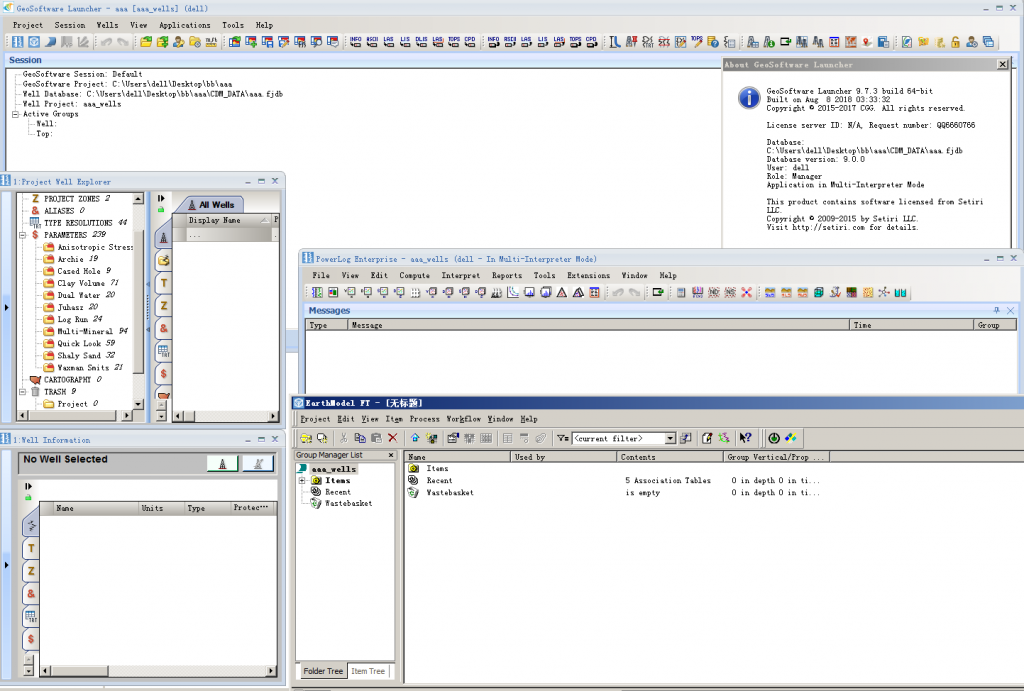
jason 9.7.3 powerlog 9.7.3
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件, й’»дә•жөӢдә•иҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә linux, win64, еҹ№и®ӯи§Ҷйў‘, жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ, й’»дә•жөӢдә•
jason 9.7.3 powerlog 9.7.3е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
ResTools
ResToolsжІ№ж°”и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢеҸҠеҠЁжҖҒеҲҶжһҗзі»з»ҹжҳҜдёҖж¬ҫзҗҶеҝөе…ҲиҝӣгҖҒеҠҹиғҪејәеӨ§зҡ„жІ№ж°”и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢеҸҠеҠЁжҖҒеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件пјҢе®һзҺ°дәҶжІ№ж°”и—ҸеҠЁжҖҒеҲҶжһҗе’ҢжІ№ж°”и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢдёҖдҪ“еҢ–з ”з©¶гҖӮ
иҪҜ件иҮҙеҠӣдәҺд»ҺжІ№и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢеёҲзҡ„е®һйҷ…дҪҝз”Ёи§’еәҰеҮәеҸ‘пјҢд»Ҙж“ҚдҪңз®ҖеҚ•гҖҒеҠҹиғҪе®Ңж•ҙзҒөжҙ»дёәзү№иүІиҝӣиЎҢз ”еҸ‘пјҢдҪҝиҪҜ件еҲҮе®һжҲҗдёәжІ№и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢеёҲ们зңҹжӯЈзҡ„еҠ©жүӢгҖӮ
ResToolsжІ№ж°”и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢеҸҠеҠЁжҖҒеҲҶжһҗзі»з»ҹеҢ…жӢ¬пјҡжІ№ж°”и—ҸеҠЁжҖҒзӣ‘жөӢпјҲ1дёӘжЁЎеқ—пјүгҖҒжІ№еұӮзү©зҗҶпјҲ8дёӘжЁЎеқ—пјҡе№іеқҮзӣёжё—жӣІзәҝгҖҒе№іеқҮжҜӣз®ЎжӣІзәҝгҖҒеҸ–иҠҜйҘұе’ҢеәҰж ЎжӯЈгҖҒPVTи®Ўз®—гҖҒзӣёжё—и®Ўз®—гҖҒжҜӣз®ЎжӣІзәҝи®Ўз®—гҖҒеҲҶжөҒйҮҸи®Ўз®—гҖҒзӣёжё—жЁЎеһӢзј–иҫ‘пјүгҖҒжІ№ж°”и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢпјҲ16дёӘжЁЎеқ—пјҡйҖ’еҮҸеҲҶжһҗгҖҒж°ҙй©ұжӣІзәҝгҖҒйҖ’еҮҸеҲҶжһҗдёҺж°ҙй©ұжӣІзәҝиҒ”з«ӢгҖҒжөҒе…ҘеҠЁжҖҒжЁЎеһӢгҖҒйңҚе°”жӣІзәҝгҖҒй”ҘиҝӣжЁЎеһӢгҖҒйҮҮ收зҺҮи®Ўз®—гҖҒжә¶и§Јж°”й©ұжІ№и—ҸеҠЁжҖҒйў„жөӢгҖҒеҗ«ж°ҙдёҺйҮҮеҮәзЁӢеәҰи®Ўз®—гҖҒеҗ«ж°ҙдёҠеҚҮ规еҫӢеҲҶжһҗгҖҒдә•зҪ‘еҜҶеәҰи®Ўз®—гҖҒж°ҙдҫөйҮҸи®Ўз®—гҖҒж°ҙй©ұжІ№ж•ҲзҺҮгҖҒж— еӣ ж¬ЎйҮҮжІ№йҮҮж¶ІжӣІзәҝи®Ўз®—гҖҒеӯҳж°ҙзҺҮи®Ўз®—гҖҒе№іеқҮең°еұӮеҺӢеҠӣи®Ўз®—)гҖҒзү©иҙЁе№іиЎЎ(2дёӘжЁЎеқ—пјҡжІ№ж°”и—Ҹзү©иҙЁе№іиЎЎи®Ўз®—гҖҒзәҜж°”и—Ҹзү©иҙЁе№іиЎЎи®Ўз®—)е…ұи®Ў24дёӘжЁЎеқ—пјҢж¶өзӣ–дәҶжІ№ж°”и—Ҹе·ҘзЁӢзҡ„еӨҡдёӘйўҶеҹҹгҖӮ
йҷӨдәҶеҠҹиғҪиҜҰз»Ҷдё°еҜҢеӨ–пјҢиҜҘиҪҜ件еңЁж•°жҚ®еӨ„зҗҶд»ҘеҸҠеӣҫеҪўжҳҫзӨәж–№йқўд№ҹжңүеҫҲеӨ§зҡ„дјҳеҠҝгҖӮйҷӨдәҶеҸҜд»Ҙд»Һoracleж•°жҚ®еә“зӣҙжҺҘеҜје…Ҙж•°жҚ®еӨ–пјҢж•°жҚ®иҫ“е…Ҙиҫ“еҮәдёҺexcelиЎЁж јзұ»дјјпјҢж”ҜжҢҒе…ЁйҖүгҖҒеӨҚеҲ¶гҖҒзІҳиҙҙеҠҹиғҪпјҢиҖҢдё”йҖ’еҮҸеҲҶжһҗзӯүжЁЎеқ—зҡ„ж•°жҚ®зӮ№еҸҜд»ҘдҫҝжҚ·ең°еҲ йҷӨе’ҢжҒўеӨҚпјҢеҠЁжҖҒзӣ‘жөӢжЁЎеқ—еҸҜд»ҘдҪҝз”ЁеӨҡиҫ№еҪўйҖүжӢ©еҚ•дә•жҲ–дә•з»„иҝӣиЎҢзӣ‘жөӢеҲҶжһҗгҖӮеӣҫеҪўе…ғзҙ пјҲж ·ејҸгҖҒйўңиүІгҖҒеқҗж ҮиҪҙж•°еҖјзӯүпјүе®Ңе…ЁејҖж”ҫпјҢз”ЁжҲ·еҸҜд»Ҙи®ҫзҪ®дёәиҮӘе·ұе–ңж¬ўзҡ„йЈҺж јпјҢ并дҝқеӯҳдёәжЁЎжқҝгҖӮ
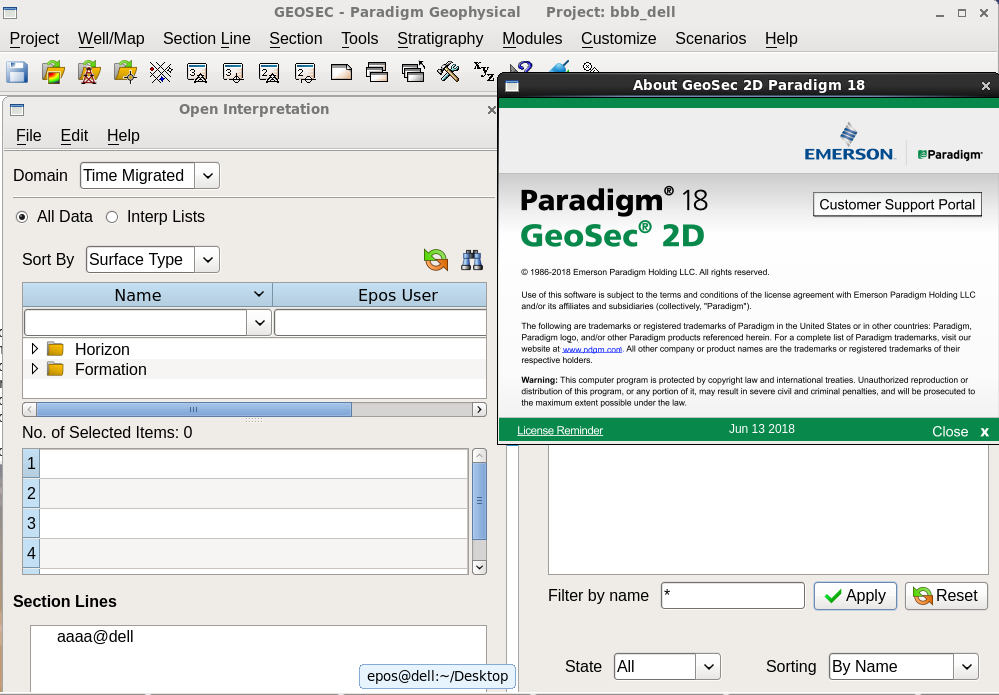
Geosec 2018
GeoSec
Fast, accurate understanding of structural history.
The Paradigm® GeoSec® multi-faceted structural geology tool provides valuable insight about the reservoir geometry and structural history of potential prospects.
With GeoSec, geoscientists and geologists can quickly incorporate structural geological analysis into exploration and production workflows. The resulting analysis assists in risk minimization and enhances the potential for locating new prospective targets.
Available through the Paradigm® SeisEarth® multi-interpretation evaluation suite, GeoSec increases understanding of tectonic behavior and structural age, while revealing flaws in the consistency of data interpretation.
GeoSec core and expanded features include:
- Integration of 3D well data with 2D projection module
- Incorporation of log curve data in structural analysis
- 2D strain analysis and stress determination
- Link to SeisEarth Section and integration with the Epos® database
- Multi-Z values for formation boundaries
- Flexible input/output, 2D/3D data exchange
- Standardized ergonomic user interface with dynamic contextual help
- Animation, movie player and snapshots
- Qt graphics enabling fast, high-quality display of fonts and graphics
- Robust interoperability for seamless access to third-party remote databases
RICH ANALYSIS OF COMPLEX REGIMES
The GeoSec tool assists in the analysis of complex tectonic regimes with a rich choice of structural analysis and restoration algorithms. As a result, geophysicists and geologists can increase their understanding of the tectonic behavior and structural age of prospects, while revealing flaws in the consistency of data interpretation.
- Compaction, decompaction, and isostatic analysisВ are used to locate the original thickness and depth of the lithological units. This analysis is necessary to estimate the amount of original porosity and depositional environment present before tectonism.
- Structural modeling and fault geometry analysisВ include algorithms for Fault Bend Fold, Fault Slip Fold, Fault Prediction, Fault Parallel Flow, Trishear Fold and Fault Propagation. These are used to generate interpretations where the resolution of the seismic data is poor or where there are few control points to generate a good model.
- The Flexural SlipВ is an algorithm that models the deformation mechanism present in many compressional tectonic regimes.
- The Vertical/Oblique SlipВ algorithm models a deformation mechanism present in many extensional tectonic regimes.
- Projection algorithmsВ for well dipmeter and borehole information calculate the apparent strike and dip along different azimuths of the cross-section. The interactive, dip-guided models deliver a more exact geological representation of the subsurface.
В ULTI-Z VALUES FOR REALISTIC GEOLOGICAL MODELS
Multi-Z values for formation boundaries are a necessity in compressional tectonic regimes in which lithological units frequently overlap. GeoSec solves this problem by supporting multiple occurrences of the same horizon at any x-y location.
Using planimeter tools and automated polygonal calculation, GeoSec also enables stratigraphically linked geological fill patterns and solid shading. This provides an accurate and comprehensive picture of the subsurface, even in very complex environments such as salt tectonic regimes with domes and intrusions.
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ е…¶е®ғ
ж Үзӯҫдёә linux, paradigm, win64, ең°йңҮи§ЈйҮҠ, жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Geosec 2018е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
Emerson Paradigm 2018.1 2019 2022 2023
 EmersonвҖҷs ParadigmВ® 18 provides a next-generation platform that includes new applications for advanced automation using machine learning methods, enhanced integration across the full range of Paradigm solutions, more effective collaboration, with applications running on the Cloud, and optimization of processes and workflows, including high-resolution seismic processing, imaging and modeling, that improve image and earth model accuracy. The following products are included in Paradigm 18: вҖў EarthStudy 360В® Full-Azimuth Imaging and Characterization вҖў EchosВ® Seismic Processing вҖў Explorer™ Time-to-Depth Conversion вҖў GeoDepthВ® Velocity Modeling and Imaging вҖў GeologВ® Formation Evaluation вҖў GeoSecВ® 2D 2D Geological Structural Restoration вҖў QSI (ProbeВ®/VanguardВ®) AVO Analysis, Seismic Inversion, and Property Determination вҖў SeisEarthВ® Multi-Survey Interpretation вҖў SKUA-GOCAD™ High-Definition Earth Modeling вҖў StratEarthВ® Geologic Interpretation вҖў StratimagicВ® Seismic Facies Classification вҖў SysdrillВ® Designer Embedded Well Planning вҖў VoxelGeoВ® Voxel-Volume Interpretation вҖў WAM Web Asset Manager This release uses Machine Learning as a data integrator and process automation tool, and introduces new solutions for the unsupervised classification of prestack and poststack seismic data. Geobody detection has been integrated into the SeisEarth interpretation solution suite and can be applied to the results of the seismic facies classification. A new parameter sensitivity analysis has been introduced in this release to facilitate user understanding of the impact of parameter changes on several interpretation workflows. Accessibility and collaboration are optimized through support for applications running on the Cloud. This gives Paradigm users another way to access our products, and makes it easier than ever for remote teams to work together. In Paradigm 18, further enhancements have been made to the Integrated Canvas released in ParadigmВ® 17, that consolidates the core SeisEarth interpretation windows (3D Canvas, BaseMap, and Section) into a single application. The Integrated Canvas is complemented with new high-resolution workflows for interval seismic, Spectral Decomposition, and Dip Steered Enhancement attributes.
EmersonвҖҷs ParadigmВ® 18 provides a next-generation platform that includes new applications for advanced automation using machine learning methods, enhanced integration across the full range of Paradigm solutions, more effective collaboration, with applications running on the Cloud, and optimization of processes and workflows, including high-resolution seismic processing, imaging and modeling, that improve image and earth model accuracy. The following products are included in Paradigm 18: вҖў EarthStudy 360В® Full-Azimuth Imaging and Characterization вҖў EchosВ® Seismic Processing вҖў Explorer™ Time-to-Depth Conversion вҖў GeoDepthВ® Velocity Modeling and Imaging вҖў GeologВ® Formation Evaluation вҖў GeoSecВ® 2D 2D Geological Structural Restoration вҖў QSI (ProbeВ®/VanguardВ®) AVO Analysis, Seismic Inversion, and Property Determination вҖў SeisEarthВ® Multi-Survey Interpretation вҖў SKUA-GOCAD™ High-Definition Earth Modeling вҖў StratEarthВ® Geologic Interpretation вҖў StratimagicВ® Seismic Facies Classification вҖў SysdrillВ® Designer Embedded Well Planning вҖў VoxelGeoВ® Voxel-Volume Interpretation вҖў WAM Web Asset Manager This release uses Machine Learning as a data integrator and process automation tool, and introduces new solutions for the unsupervised classification of prestack and poststack seismic data. Geobody detection has been integrated into the SeisEarth interpretation solution suite and can be applied to the results of the seismic facies classification. A new parameter sensitivity analysis has been introduced in this release to facilitate user understanding of the impact of parameter changes on several interpretation workflows. Accessibility and collaboration are optimized through support for applications running on the Cloud. This gives Paradigm users another way to access our products, and makes it easier than ever for remote teams to work together. In Paradigm 18, further enhancements have been made to the Integrated Canvas released in ParadigmВ® 17, that consolidates the core SeisEarth interpretation windows (3D Canvas, BaseMap, and Section) into a single application. The Integrated Canvas is complemented with new high-resolution workflows for interval seismic, Spectral Decomposition, and Dip Steered Enhancement attributes.
Paradigm 18 introduces a вҖңStratigraphic ContextвҖқ for a variety of interpretation activities. This new functionality groups together user selections of well data activity, marker priority, and assignment, with the Epos Formation Table. It enables users to easily switch between different combinations of any of the above through a simple one-step mechanism, and to share their data selections easily with colleagues. Integration between interpretation and modeling applications has been extended in Paradigm 18. In this release, the main Interpretation windows share a common user interface with SKUA-GOCAD, for more efficient work. Time-based production data loaded in EposВ® may now be accessed by StratEarth and SKUA-GOCAD, enabling a more comprehensive analysis of this data within the interpretation framework. StratEarth is also available in the same window used by BaseMap, 3D Canvas, and Section, to improve the experience of geologists working in the Epos environment. QSI (Probe/Vanguard) has been enhanced and now includes automatic parameter optimization at all well locations for seismic inversion and AVO(A) activities. New rock physics template creation and display are now available in the crossplot utility. Users can access rock physics templates from the Epos database or from Geolog. For GeoDepth velocity model building users, tomography updates include support for large datasets in conjunction with high-resolution tomographic update grids. This leads to a substantial reduction in memory consumption and project run times, while resulting in more accurate velocity models. The integration between GeoDepth and SKUA has been further strengthened by enhancements to GeoDepth 3D structural model-based tomography, made to support geologically constrained velocity models that honor faults and multi-valued surfaces. Additionally, a time-preserving tomography workflow supports complex models, facilitating the minimization of mis-ties between well markers and the structural model in depth. GeoDepth users will enjoy productivity improvements when performing velocity model updating and imaging of multi-line 2D projects, including a new 2D Kirchhoff depth migration, 2D illumination studies, and others. A new orthorhombic workflow is now available for output from EarthStudy 360 Imager, enabling more accurate estimation of fracture orientation and stress. New features for users of Echos include a method for model-based ground roll modeling and attenuation based on estimation of near surface parameters, new residual statics applications, and an alternative method for 5D data reconstruction based on Radon Transform data modeling for improved signal representation. New workflows and tools leverage modern workstations for the graphical display, analysis, quality control, and manipulation of seismic survey geometry information. And new seismic file parallel I/O capabilities provide improved throughput for seismic processing and imaging workflows. SKUA-GOCAD modeling workflows have been optimized to handle large numbers of wells. Additional functionality for unflattening interpretation data and seismic volumes has been added to better benefit from SKUA-GOCAD paleospace. Also in SKUA-GOCAD, gridless geostatistics have been added for stratigraphically constrained property modeling on unstructured grids and meshless objects. The release upgrades its support for geomechanical workflows with hybrid grids that combine the benefits of structured and unstructured grids, in support of both flow simulation and geomechanical simulation workflows.
A significant upgrade to Geolog 18 is the generalization of petrophysical uncertainty, which enables most Geolog modules and Loglans to run in Monte Carlo mode. Other updates include a new customized reporting module, a Formation Testing methodology, and major updates to the geomechanics, engineering, and production modules, including a new cement evaluation functionality. Python programming support is also enabled inside Geolog Loglan. In Paradigm 18, access to Web-based Open Source and GIS data sources has been extended. A new mechanism that allows the automatic distribution of вҖңapprovedвҖқ support packs to all Windows users of Paradigm applications offers significant benefits to large deployments. This release offers very high levels of prestack seismic data compression, with no significant degradation of the seismic data signal. We develop products in collaboration with our customers, with the main goal of enhancing the user experience and outcomes. In Paradigm 18, as in other recent releases, we have significantly expanded our investment in quality assurance, including extensive internal and beta testing. This, together with the technical depth of our solutions, is aimed at providing you with the best technologies for safe, reliable, and profitable extraction of the earth’s minerals. Your success is our highest priority. We encourage you to explore the many new features of Paradigm 18, and we look forward to your continued suggestions for improving our product lines.
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件, ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件, ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件, жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә linux, win64, ең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件, ең°йңҮеӨ„зҗҶ, ең°йңҮи§ЈйҮҠ, еҹ№и®ӯи§Ҷйў‘, жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Emerson Paradigm 2018.1 2019 2022 2023е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
Seisware 9.1
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, ең°йңҮи§ЈйҮҠ, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Seisware 9.1е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
flatirons 18.02
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, ең°йңҮеӨ„зҗҶ, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
flatirons 18.02е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
Greenmountaion mesa 15
Version 15.0 Enhancements and Fixes
1. Window size, geometry and zoom levels can now be saved as views. Saved views allow you to return to previous states of the program which greatly simplifies the process of capturing screens for reports and presentations. Views can also be shared between different projects. If you are evaluating multiple survey designs for a project, the saved view feature gives you the ability to make equivalent screen captures across all of the projects.
2. A screenshot button has been added to the zoom toolbar. This button allows you to quickly capture the current window and save it to either the Windows clipboard or to a PNG file.
3. Elevation dependent fold calculations now have a function for creating a downgoing sea-air multiple for marine and ocean bottom surveys. Fold calculations can contain either the upgoing reflection, the downgoing multiple, or both events in the same calculation.
4. The line/brick layout now has an option for creating flip-flop source geometries.
5. Marine boat configurations now have the ability to define a source depth and a streamer depth. Slanted cable geometries are also supported.
6. Marine shooting now supports simultaneous source shooting geometries.
7. A new source point consolidation tool allows you to merge co-located source points into a single source with a merged template.
8. Discrete range color scales now display a histogram of the data distribution of the current display as well as a numerical percentage. The histogram dynamically updates as the zoom level changes in the window.
9. There is a new raytracing mode named illumination raytracing. Illumination rays are exploding reflector raypaths similar to the Smart Aperture tool. The major difference is that illumination raytracing is done for every grid location on a model horizon. Instead of testing individual locations on a horizon and shooting a single cone of 30 degree exploding reflector raypaths, illumination raytracing shoots a dense cone of rays out to the critical angle (or other user defined take off angle) across the entire horizon. The resulting diagnostics allow you to analyze the source-receiver maximum offset required across an entire model. You can also analyze where imaging may be problematic–even with full azimuth sampling. Illumination rays are generated in the Raytracer application
10. The illumination raytracing feature comes with two new modes of interactive raytracing. Illumination analysis mode has a mode for modeling “test shots.” You can click the mouse on a location and shoot a cone of rays into the model. The emergence points of the raypaths will be displayed so you can analyze the effects of the model and get a sense for the size of the proper recording patch. The test shot raypaths can also be viewed in the 3D window. The second interactive raytracing mode allows you to see the results of the illumination raytracing on a grid node by grid node basis.
11. Offset raytracing attributes can now be limited by takeoff, incidence and emergence angle. Bin limits can also be applied to the offset raytracing attribute calculations.
12. Depth slices from MESA Expert velocity models can be displayed as contour maps in the Design Window.
13. Velocity models can be viewed as x, y, and depth slices in the 3D window.
14. MESA Expert attributes calculated from offset, normal and image raytracing can be exported to ASCII CSV files.
15. ASCII files containing an xy-coordinate and a data value can be converted into a GeoTIFF file for use with the data raster display and analysis tools.
16. Parameters formerly set as environmental variables have been replaced with project-independent user preferences set inside of MESA. User preferences control the default data directory, the locations of the color scale and configuration files, and whether or not to display the release notes at startup.
17. Source and receiver attributes can be calculated from offset raytracing results. These attributes include fold, mean amplitude and mean travel time. Previously, all offset raytracing attributes were CRP-based.
18. A calculator has been added to the project statistics to show the number of channels needed for a specified range of receiver lines.
19. The source and receiver count has been added to the toolbar in edit templates mode.
20. Source and receiver numbering options have been added to the unit template layout tool.
21. Marine point counts and line lengths are now included on the project summary tab of the survey statistics.
22. Marine project size has been expanded from 2 billion traces to 4 billion traces.
23. Numeric fold display option will change label color from black to white depending on the darkness of the fold color in a bin. Dynamic sizing was also added to these labels.
24. MESA will now reopen in the same screen location as when it was last closed.
25. Improved symbol sizing in the 3D window.
Bug fixes
26. Fixed a printing problem. When printing to PDF, the first plot would work fine but subsequent print jobs would produce zero length plots or MESA would hang.
27. Fixed crashes in Model Builder related to cross section creation.
28. Fixed a problem merging marine projects using imported P190 data or using marine sail polylines.
29. The first marine source in an imported P190 data set was incorrectly getting flagged as dead.
30. Fixed an issue with temporary databases when multiple instances of MESA are running.
31. Fixed an issue during fold calculations when the reciprocal/redundancy limits were used in conjunction with other limiting options.
32. Fixed an issue with the unit template window crashing if all shooting configurations have been deleted.
33. Fixed a Shapefile reading problem when the polygon vertices were ordered incorrectly.
34. Fixed an issue with occasional template positioning errors after merging surveys.
35. Fixed an issue with inline and crossline offset limits applied during fold calculations on rotated surveys.
36. Fixed a drawing bug with displaying the line connecting receivers after exiting an editing mode.
37. Fixed an issue with source and receiver labels disappearing at certain zoom levels.
38. Improved the calculation of model dips in the model attribute generation tool.
39. Fixed a crash in unit template window when copying/moving templates with the receiver checkbox unselected.
40. Changed the wording of the anchor point controls in the source/receiver line layout dialog when filling a region.
41. Fixed a problem smoothing horizons in Model Builder.
42. Fixed a visibility problem when toggling on/off points when multiple projects are loaded.
43. Fixed a problem with the opacity controls for bin attribute diagrams.
44. Fixed a problem when creating more than one survey boundary exclusion zone.
45. Fixed a display problem when highlighting the sources firing into a selected receiver and scrolling the display.
46. Changed the wording on the data raster menus to clarify the difference between images and data GeoTIFF files.
47. Fixed a problem with the working directory getting set incorrectly after cycling through color scale choices.
48. Fixed a problem with direct arrivals and gradient velocity models for VSP geometries.
49. Fixed an issue displaying bin attributes in the 3D window.
50. Fixed a symbol size problem in the legend.
51. Fixed a crash opening a spreadsheet before a survey is created.
52. Fixed a crash opening the 3D window when horizon contours are being displayed in the Design Window.
53. Fixed problems loading saved discrete color scales.
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ
ж Үзӯҫдёә greenmountian, win64, ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Greenmountaion mesa 15е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
GMseis 3.4
GMSeis V3.4 йқҷж ЎжӯЈиҪҜ件еҠҹиғҪз®Җд»ӢеҸҠзү№зӮ№
—еҲ©з”Ёе…Ҳиҝӣзҡ„Java жҠҖжңҜејҖеҸ‘и·Ёе№іеҸ°зҡ„еӣҫеҪўз•Ңйқўж–№ејҸ
—еӣҫеҪўз•ҢйқўеҸӢеҘҪ,зҒөжҙ»,жҳ“еӯҰжҳ“жҮӮ,ж“ҚдҪңдҪҝз”Ёйқһеёёж–№дҫҝ
—иғҪеҒҡ40000йҒ“/зӮ®зҡ„и¶…еӨ§и®°еҪ•;44дёҮзӮ®,15000йҒ“/зӮ®
—иҪҜ件иғҪеҒҡжңҖеӨ§дёҠйҷҗпјҡ
shot 2,000,000
channel/shot 65,500
Receiver points 160,770,000
Max total traces 4,000,000,000пјҲе·ІеҒҡиҝҮпјү
—еҝ«йҖҹ并иЎҢиҝҗз®—:
иғҪеңЁйӣҶзҫӨжңәеҷЁдёҠ并иЎҢиҝҗз®—пјҢд№ҹиғҪеңЁзӣ®еүҚжөҒиЎҢзҡ„еӨҡж ёPCжңәдёҠ并иЎҢиҝҗз®—пјҢеҸҜ并иЎҢеӨ„зҗҶи¶…еӨ§ж•°жҚ®дҪ“, жһҒеӨ§жҸҗй«ҳдәҶеҚіж—¶еӨ„зҗҶеҚіж—¶жҳҫзӨәзҡ„ж•ҲзҺҮ,иҠӮзңҒж—¶й—ҙ, йҷҚдҪҺжҲҗжң¬
—еӨҡз§Қйқҷж ЎжӯЈз»јеҗҲжұӮи§Јж–№жЎҲ
–еҲ©з”ЁеҲқиҮіпјҡз»ҝеұұ, иҜ»йҒ“еӨҙ, ASCIIж–Ү件, е…¶е®ғ
–еҝ«йҖҹзҡ„иҮӘеҠЁжӢҫеҸ–еҲқиҮіеҸҠдәӨдә’жӢҫеҸ–еҲқиҮі
–жЁЎеһӢжі•йқҷж ЎжӯЈ +жҠҳе°„еү©дҪҷйқҷж ЎжӯЈ
–еұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”жі•йқҷж ЎжӯЈ+жҠҳе°„еү©дҪҷйқҷж ЎжӯЈ
–йҮҺеӨ–еҫ®жөӢдә•жЁЎеһӢжі•+жҠҳе°„еү©дҪҷйқҷж ЎжӯЈ
–е…¶е®ғиҪҜ件йқҷж ЎжӯЈ +жҠҳе°„еү©дҪҷйқҷж ЎжӯЈ
–CMP еҸҚе°„еү©дҪҷйқҷж ЎжӯЈ
–еҝ«йҖҹзҡ„йқҷж ЎжӯЈQCпјҡ еҚ•зӮ®жҲ–д»»ж„ҸдҪҚзҪ®еҸ еҠ еү–йқў
–еҠ еҫ®жөӢдә•зәҰжқҹеҸҚжј”йҖҹеәҰпјҢжӣҙеҘҪең°и§ЈеҶіеӨҚжқӮең°еҢәйқҷж ЎжӯЈй—®йўҳ
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә win32, win64, ең°йңҮеӨ„зҗҶ, еҹ№и®ӯи§Ҷйў‘, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
GMseis 3.4е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
tomodel 8.0
гҖҠеӨҚжқӮжҺўеҢәиҝ‘ең°иЎЁе»әжЁЎе’Ңж ЎжӯЈзі»з»ҹ ToModelгҖӢдё“й—Ёй’ҲеҜ№еӨҚжқӮиҝ‘ең°иЎЁжҺўеҢәең°йңҮеӢҳжҺўиҖҢз ”еҲ¶пјҢ
еҢ…жӢ¬еҲқиҮіжіўеұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”е»әз«Ӣй«ҳзІҫеәҰиҝ‘ең°иЎЁйҖҹеәҰжЁЎеһӢе’ҢеҲқиҮіжіўеү©дҪҷйқҷж ЎжӯЈйҮҸи®Ўз®—пјҢжҸҗдҫӣдё°еҜҢйқҷж Ў
жӯЈиҙЁйҮҸжҺ§еҲ¶дҪ“зі»гҖӮToModel жҳҜдёҖдёӘд»ҺйҮҺеӨ–йҮҮйӣҶеҲ°е®ӨеҶ…еӨ„зҗҶпјҢеӨҡз§Қиө„ж–ҷдә’иЎҘпјҢеӨҡз§Қз®—жі•дә’иЎҘпјҢ
д»Ҙе»әз«ӢеҮҶзЎ®иҝ‘ең°иЎЁйҖҹеәҰжЁЎеһӢдёәж ёеҝғ,и§ЈеҶіеӨҚжқӮжҺўеҢәиҝ‘ең°иЎЁй—®йўҳзҡ„иҪҜ件系з»ҹгҖӮ
жҠҖжңҜзү№иүІжңүпјҡ
1пјүйҮҮз”ЁеҹәдәҺжіўеҠЁж–№зЁӢзҡ„еҝ«йҖҹжӯҘиҝӣжіўеүҚиҝҪиёӘжҠҖжңҜпјҢе®һзҺ°е°ҸзҪ‘ж је»әжЁЎпјҢеҸҚжј”з»“жһңзІҫеәҰй«ҳпјҢи®Ў
з®—ж•ҲзҺҮй«ҳгҖӮ
2пјүйҮҮз”ЁвҖңжүҒвҖқзҪ‘ж је»әжЁЎпјҢиҖҢдёҚжҳҜжӯЈж–№еҪўпјҢжҸҗй«ҳеҜ№з•Ңйқўзҡ„еҲ»з”»иғҪеҠӣпјҢд»ҺиҖҢжҸҗй«ҳж·ұеәҰж–№еҗ‘зҡ„
еҲҶиҫЁзҺҮгҖӮ
3пјүе°Ҷе°ҸжіўеҸҳжҚўеә”з”ЁдәҺеұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”пјҢжҸҗй«ҳеҸҚжј”зІҫеәҰгҖӮ
4пјүвҖңж— зјқжӢјжҺҘвҖқдёүз»ҙеұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”жҠҖжңҜпјҢе®ҢжҲҗи¶…еӨ§и§„жЁЎдёүз»ҙжҲ–иҖ…иҝһзүҮдёүз»ҙзҡ„еұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”иҝ‘ең°иЎЁ
е»әжЁЎгҖӮ
5пјүйҮҮз”ЁйқһзәҝжҖ§еҸҚжј”з®—жі•пјҢеҫ—еҲ°е…ЁеұҖжңҖдјҳи§ЈпјҢеҸҚжј”з»“жһңеҹәжң¬дёҚдҫқиө–дәҺеҲқе§ӢйҖҹеәҰжЁЎеһӢгҖӮ
6пјүжҸҗдҫӣй…ҚеҘ—зҡ„йқҷж ЎжӯЈи®Ўз®—жөҒзЁӢпјҢеҹәдәҺеұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”иҝ‘ең°иЎЁйҖҹеәҰжЁЎеһӢпјҢи®Ўз®—еҹәеҮҶйқўйқҷж ЎжӯЈйҮҸпјӣ
然еҗҺпјҢдҪҝз”ЁеҲқиҮіжіўеү©дҪҷйқҷж ЎжӯЈж–№жі•и®Ўз®—зҹӯжіўй•ҝйқҷж ЎжӯЈйҮҸпјҢToModel еҚіеҸҜдҝқиҜҒеҮҶзЎ®зҡ„жһ„йҖ еҪўжҖҒпјҢ
еҸҲеҸҜеҫ—еҲ°й«ҳиҙЁйҮҸзҡ„еҸ еҠ жҲҗеғҸеү–йқўгҖӮ
7пјүиҮӘйҖӮеә”зәҰжқҹеұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”жҠҖжңҜпјҢе°Ҷе°ҸжҠҳе°„е’Ңеҫ®жөӢдә•еҫ—еҲ°зҡ„й«ҳзІҫеәҰжһҒжө…еұӮйҖҹеәҰпјҢз”ЁдәҺзәҰжқҹеӨ§
зӮ®еҲқиҮіеұӮжһҗеҸҚжј”пјҢжҸҗй«ҳеҸҚжј”зҡ„зІҫеәҰгҖӮ
8пјүйҮҮз”ЁвҖңдәәжҖ§еҢ–вҖқи®ҫи®ЎпјҢиҪҜ件结жһ„з®ҖжҙҒпјҢжҳ“еӯҰжҳ“з”ЁгҖӮ
йҖӮз”Ёд»ҺдәӢең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶгҖҒеӨ„зҗҶе’Ңи§ЈйҮҠзҡ„жңүе…іеҚ•дҪҚе’Ңдәәе‘ҳгҖӮ
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, ең°йңҮеӨ„зҗҶ, еҹ№и®ӯи§Ҷйў‘, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
tomodel 8.0е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
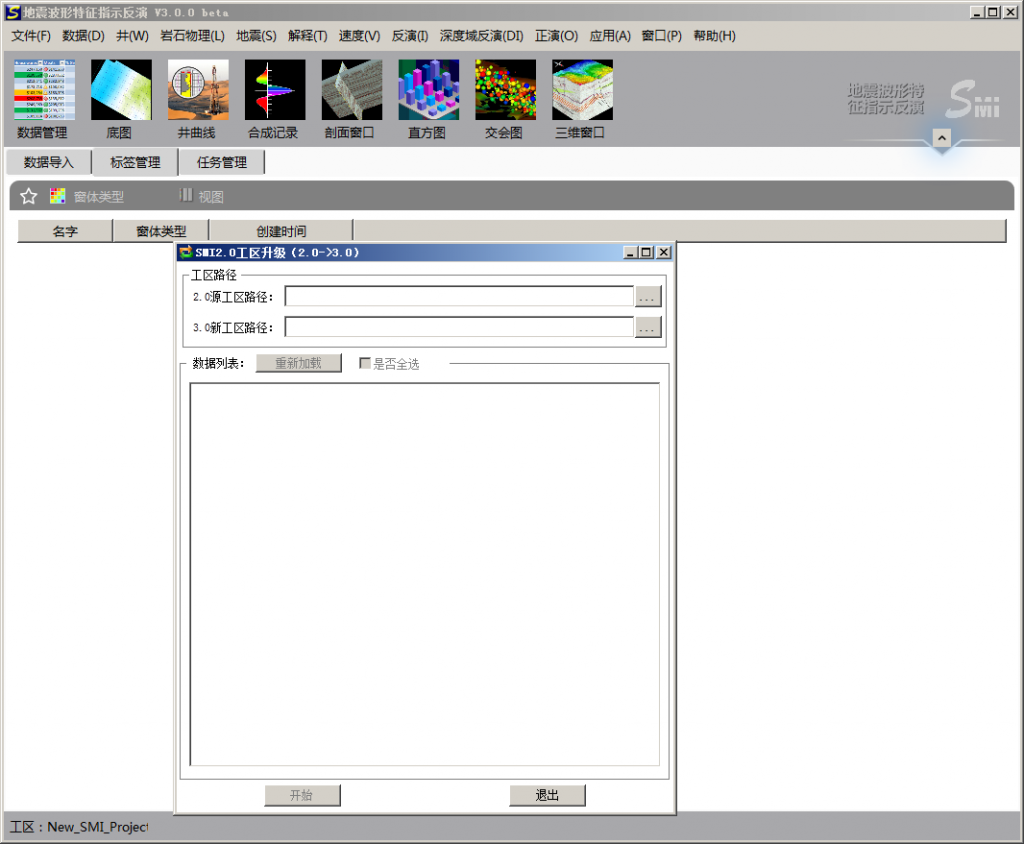
Pegete SMI 3.0
Pegete SMI 2.1
seino smi 2.1
 В В Pegete SMI 3.0
В В Pegete SMI 3.0
seino smi 3.0
жіўйҳ»жҠ—еҸҚжј”жҠҖжңҜеңЁеӢҳжҺўејҖеҸ‘дёӯзҡ„еә”з”Ёе·Із»Ҹжңү20еӨҡе№ҙзҡ„еҺҶеҸІдәҶпјҢеҸ‘еұ•дәҶд»ҺзЎ®е®ҡжҖ§еҸҚжј”еҲ°ең°иҙЁз»ҹи®ЎеӯҰйҡҸжңәеҸҚжј”зӯүеӨҡз§Қж–№жі•гҖӮйҡҸзқҖжІ№з”°еӢҳжҺўгҖҒејҖеҸ‘е·ҘдҪңзҡ„иҝӣеұ•пјҢеҜ№еӮЁеұӮйў„жөӢзҡ„зІҫеәҰиҰҒжұӮд№ҹи¶ҠжқҘи¶Ҡй«ҳпјҢдј з»ҹзҡ„常规еҸҚжј”ж–№жі•е·Іж— жі•ж»Ўи¶ій«ҳзІҫеәҰеӮЁеұӮйў„жөӢзҡ„иҰҒжұӮдәҶгҖӮе°Өе…¶жҳҜйҷҶзӣёзӣҶең°жҷ®йҒҚеҸ‘иӮІеӨҚжқӮз»“жһ„еӮЁеұӮпјҢеҰӮжІійҒ“гҖҒж»©еққзӯү,еҚ•еұӮеҺҡеәҰе°ҸпјҢжЁӘеҗ‘еҸҳеҢ–еҝ«пјҢеҲҶеёғ规еҫӢеӨҚжқӮгҖӮиҰҒиҗҪе®һжҺўжҳҺеӮЁйҮҸпјҢдјҳеҢ–ејҖеҸ‘ж–№жЎҲпјҢи®ҫи®Ўж°ҙе№ідә•иҪЁиҝ№д»ҘеҸҠеҲҶжһҗжіЁйҮҮе…ізі»пјҢеҜ»жүҫеү©дҪҷжІ№жҪңеҠӣзӯүпјҢиҰҒжұӮеӮЁеұӮз ”з©¶еҜ№иұЎзІҫзЎ®еҲ°е°ҸеұӮжҲ–еҚ•з ӮдҪ“пјҢеӣ жӯӨй«ҳзІҫеәҰеӮЁеұӮеҸҚжј”жҠҖжңҜжҲҗдёәеҲ¶зәҰзІҫз»ҶеӢҳжҺўе’ҢејҖеҸ‘зҡ„е…ій”®гҖӮзӣ®еүҚй«ҳеҲҶиҫЁзҺҮеҸҚжј”ж–№жі•дё»иҰҒеә”з”Ёең°иҙЁз»ҹи®ЎеӯҰйҡҸжңәеҸҚжј”пјҢеҜ№дә•дҪҚеқҮеҢҖеҲҶеёғиҰҒжұӮиҫғй«ҳпјҢдё”еҸҚжј”з»“жһңйҡҸжңәжҖ§ејәпјҢе№ійқўеҲҶиҫЁзҺҮдҪҺпјҢз”ҹдә§дёӯйҡҫд»Ҙе№ҝжіӣжҺЁе№ҝеә”з”ЁгҖӮ
вҖңең°йңҮжіўеҪўзү№еҫҒжҢҮзӨәеҸҚжј”SMIВ®вҖқжҳҜеҢ—дә¬дёӯжҒ’еҲ©еҚҺзҹіжІ№жҠҖжңҜз ”з©¶жүҖжңҖж–°з ”еҸ‘зҡ„й«ҳзІҫеәҰеӮЁеұӮеҸҚжј”жҠҖжңҜпјҢйҮҮз”ЁзӢ¬еҲӣзҡ„вҖңең°йңҮжіўеҪўжҢҮзӨә马尔科еӨ«й“ҫи’ҷзү№еҚЎжҙӣйҡҸжңәжЁЎжӢҹпјҲSMCMCпјүвҖқдё“еҲ©з®—жі•пјҢеңЁең°йңҮжіўеҪўзҡ„й©ұеҠЁдёӢпјҢжҢ–жҺҳзӣёдјјжіўеҪўеҜ№еә”зҡ„жөӢдә•жӣІзәҝдёӯи•ҙеҗ«зҡ„е…ұжҖ§з»“жһ„дҝЎжҒҜпјҢиҝӣиЎҢең°йңҮе…ҲйӘҢжңүйҷҗж ·зӮ№жЁЎжӢҹгҖӮ SMIе’Ңдј з»ҹзҡ„ең°иҙЁз»ҹи®ЎеӯҰеҸҚжј”зӣёжҜ”пјҢе…·жңүзІҫеәҰй«ҳгҖҒеҸҚжј”з»“жһңйҡҸжңәжҖ§е°Ҹзҡ„зү№зӮ№пјҢдё”жӣҙеҘҪең°дҪ“зҺ°дәҶвҖңзӣёжҺ§вҖқзҡ„жҖқжғіпјҢдҪҝеҸҚжј”з»“жһңд»Һе®Ңе…ЁйҡҸжңәиө°еҗ‘дәҶйҖҗжӯҘзЎ®е®ҡпјҢеҸҜд»ҘдёәеӮЁеұӮй«ҳзІҫеәҰйў„жөӢжҸҗдҫӣжӣҙеҘҪзҡ„жҠҖжңҜи§ЈеҶіж–№жЎҲгҖӮ
вҖңSMIВ®й«ҳзІҫеәҰеҸҚжј”иҪҜ件вҖқйӣҶжҲҗдәҶ12е№ҙең°еӯҰиҪҜ件平еҸ°з ”еҸ‘з»ҸйӘҢпјҢйҮҮз”ЁдәҶжӣҙеҗҲзҗҶзҡ„еә•еұӮжһ¶жһ„пјҢжҸҗдҫӣдәҶдёҖж•ҙеҘ—е®Ңе–„зҡ„дә•йңҮз»“еҗҲеӮЁеұӮйў„жөӢжҠҖжңҜи§ЈеҶіж–№жЎҲе’Ңе·Ҙе…·пјҢеҢ…жӢ¬жөӢдә•иө„ж–ҷеҲҶжһҗгҖҒи§ЈйҮҠгҖҒең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷжһ„йҖ з ”з©¶гҖҒеұһжҖ§жҸҗеҸ–еҸҠеә”з”ЁгҖҒең°йңҮжіўеҪўжҢҮзӨәеҸҚжј”гҖҒеӮЁеұӮеҸӮж•°жЁЎжӢҹзӯүеҠҹиғҪгҖӮ
SMIиҪҜ件йҮҮз”Ёдёӯж–Үз•ҢйқўпјҢWindowsж“ҚдҪңзі»з»ҹпјҢдёүз»ҙеҸҜи§ҶеҢ–зҺҜеўғпјҢжҳ“еӯҰжҳ“з”ЁпјҢж•°еҚҒдҪҚең°иҙЁе·ҘзЁӢеёҲе…ұеҗҢеҸӮдёҺиҪҜд»¶з ”еҸ‘и®ҫи®ЎпјҢжӣҙз¬ҰеҗҲең°иҙЁе·ҘзЁӢеёҲдҪҝз”Ёд№ жғҜгҖӮй’ҲеҜ№жІ№з”°еҢәеқ—дә•ж•°йҮҸеӨҡгҖҒе·ҘдҪңйҮҸеӨ§зҡ„зү№зӮ№пјҢдё“й—Ёи®ҫи®ЎдәҶдә•жӣІзәҝиҮӘеҠЁеҹәзәҝж ЎжӯЈгҖҒжү№йҮҸж ҮеҮҶеҢ–гҖҒж— еӯҗжіўеҸҚжј”гҖҒиҮӘеҠЁеҢ№й…Қж Үе®ҡж—¶ж·ұе…ізі»зӯүе·Ҙе…·жЁЎеқ—пјҢеӨ§еӨ§иҠӮзңҒдәҶз”ЁжҲ·зҡ„ж—¶й—ҙпјҢжҸҗй«ҳдәҶеҸҚжј”е·ҘдҪңж•ҲзҺҮпјҢе°Өе…¶йҖӮеҗҲжІ№з”°з ”з©¶йҷўгҖҒйҮҮжІ№еҺӮең°иҙЁе·ҘзЁӢеёҲдҪҝз”ЁгҖӮ
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Pegete SMI 3.0е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
Sercel e428V5.0
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ
ж Үзӯҫдёә linux, ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Sercel e428V5.0е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
KAPPA Workstation 5.20
KAPPA is the leading provider ofВ Dynamic Data AnalysisВ software, training and consulting services. Data are analysed on whatever scale is available, from high frequency, high resolution transient data through low frequency, low resolution rate data in production analysis and on into full field history matching and vertical description using production log and formation test analysis. Released in 2016, Generation 5 speeds workflows, connectivity and provides a powerful platform for the future and automation.
KAPPA-WorkstationВ is an integrated engineering suite which offers analysis and modeling tools for reservoir dynamic data. Our clients told us to вҖҳthink open and think bigвҖҰвҖҷ For this reason, Generation 5 is fully 64-bit, it uses parallel processing for todayвҖҷs multicore processors and data is fully integrated between KAPPA modules and other programs via OpenServer.
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ йҮҮжІ№иҜ•дә•еҺӢиЈӮ
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ, йҮҮжІ№иҜ•дә•еҺӢиЈӮ
KAPPA Workstation 5.20е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
Seismic Processing Workshop 3.4 SPW 3.4
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷеӨ„зҗҶиҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, ең°йңҮеӨ„зҗҶ, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Seismic Processing Workshop 3.4 SPW 3.4е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
Testif-i v2.07a
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷйҮҮйӣҶ, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
Testif-i v2.07aе·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
epoffice 2017 v7
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件, жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә linux, win64, ең°йңҮи§ЈйҮҠ, еҹ№и®ӯи§Ҷйў‘, жӯЈжј”еҸҚжј”иҪҜ件, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
epoffice 2017 v7е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
TENDDEKA FloQuest 7.5
Introduction
FloQuest is a visualization application for DTS data, DAS data, Gauge data and near-wellbore modeling.
FloQuest8дә•дёӯе…үзәӨ
дә•дёӯзҡ„е…үзәӨжҠҖжңҜдҪҝж“ҚдҪңе‘ҳиғҪеӨҹеҮҶзЎ®пјҢйў‘з№Ғең°зӣ‘жөӢдә•зӯ’дёӯжөҒдҪ“зҡ„жё©еәҰгҖӮе…үзәӨз”өзјҶжІҝдә•зҡ„ж•ҙдёӘй•ҝеәҰд»Ҙ0.5зұізҡ„й—ҙйҡ”жҸҗдҫӣй«ҳеҲҶиҫЁзҺҮж•°жҚ®пјҢз”ЁдәҺжЈҖжөӢдә•зӯ’еҶ…жҲ–йҷ„иҝ‘зҡ„жөҒдҪ“жөҒеҠЁгҖӮ
DTS ж°ёд№…е®үиЈ…з”ЁдәҺжІ№дә•зӣ‘жөӢжҲ–дёҙж—¶йғЁзҪІз”ЁдәҺжІ№дә•зӣ‘жөӢпјҢдёәжі„жјҸжЈҖжөӢгҖҒз”ҹдә§дјҳеҢ–е’ҢжөҒйҮҸеҲҶй…ҚжҸҗдҫӣжңүд»·еҖјзҡ„ж•°жҚ®гҖӮ
FloQuestжҳҜеҠҹиғҪејәеӨ§зҡ„еҸҜи§ҶеҢ–е’Ңе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件пјҢе®ғдҪҝз”Ёдё“жңүз®—жі•е’Ңзӣҙи§Ӯзҡ„з•Ңйқўе°ҶеҲҶеёғејҸж•°жҚ®дёҺеӨҡдёӘж•°жҚ®жәҗж— зјқйӣҶжҲҗеҲ°жё…жҷ°зҡ„и§Ҷи§үиҫ“еҮәдёӯгҖӮ
FloQuestжҳҜдёҖдёӘз”ЁжҲ·еҸӢеҘҪдҪҶеҠҹиғҪйқһеёёејәеӨ§зҡ„Windowsеә”з”ЁзЁӢеәҸпјҢе®ғе…Ғи®ёдҪҝз”Ёе…үзәӨж•°жҚ®д»ҘеҸҠзӮ№ж•°жҚ®е’ҢеҺҶеҸІдә•дҝЎжҒҜжқҘеҮҶзЎ®е®ҡд№үпјҢе»әжЁЎе’ҢиЎҢиҝӣдә•зӯ’гҖӮ
иҝҷз§ҚзҒөжҙ»дё”еҸҜй…ҚзҪ®зҡ„иҪҜ件жҳҜе®һж—¶зӣ‘жөӢе’ҢиҜҰз»Ҷи§ЈйҮҠзҡ„зҗҶжғіе·Ҙе…·пјҢеҸҜжҸҗдҫӣеҚіж—¶еҸҜи§ҶеҢ–е’Ңдә•зӯ’йҷ„иҝ‘еӨҡзӣёжөҒе…Ҙе»әжЁЎгҖӮ
еә”з”Ё
гҖӢгҖӢзӣ‘жөӢжІ№дә•жҖ§иғҪ
гҖӢгҖӢзЎ®е®ҡжөҒе…ҘиҙЎзҢ®
гҖӢгҖӢдјҳеҢ–з”ҹдә§е’ҢжіЁеЎ‘зі»з»ҹ
гҖӢгҖӢиҜҶеҲ«жІ№дә•е®Ңж•ҙжҖ§й—®йўҳ
гҖӢгҖӢзӣ‘жҺ§ж°”дёҫйҳҖжҖ§иғҪ
гҖӢгҖӢжөӢйҮҸж–ӯиЈӮжҖ§иғҪ
гҖӢгҖӢдјҳеҢ–й…ёеҲәжҝҖ
TENDEKA ReQuest 7.5
Introduction
The guide describes ReQuest and its usage.
ReQuest is a visualization application for DTS data, DAS data, Gauge and Log data.
landmark Nexus VIP
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ ең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә landmark, linux, win64, ең°иҙЁе»әжЁЎиҪҜ件, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
landmark Nexus VIPе·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә
PaleoScan 2018.1
еҸ‘иЎЁеңЁ е…¶е®ғ, ең°йңҮиө„ж–ҷи§ЈйҮҠиҪҜ件
ж Үзӯҫдёә win64, ең°йңҮи§ЈйҮҠ, иҜ•з”ЁзүҲ
PaleoScan 2018.1е·Іе…ій—ӯиҜ„и®ә